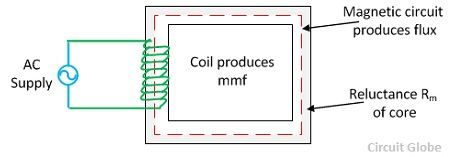
Magnetic Reluctance
Definition: The obstruction offered by a magnetic circuit to the magnetic flux is known as reluctance. As in electric circuit, there is resistance similarly in the magnetic circuit, there is a reluctance, but resistance in an electrical circuit dissipates the electric energy and the reluctance in magnetic circuit stores the magnetic energy. Also in an electric circuit, the electric field provides the least resistance path to the electric current. Similarly, the magnetic field causes the least reluctance path for the magnetic flux. It is denoted by S.
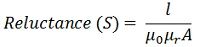
Where, l – the length of the conductor
μo – permeability of vacuum which is equal to the 4π Χ107 Henry/metre.
μr – relative permeability of the material.
A – cross-section area of the conductor.
μo – permeability of vacuum which is equal to the 4π Χ107 Henry/metre.
μr – relative permeability of the material.
A – cross-section area of the conductor.
The SI unit of magnetic reluctance is AT / Wb (ampere-turns / Weber).The reluctance of the magnetic circuit is directly proportional the length of the conductor and inversely proportional to the cross-section area of the conductor. The reciprocal of the magnetic reluctance is known as the magnetic permeance. It is given by the expression 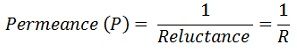
The reluctance in the DC field is defined as the ratio of the magnetic motive force and to the magnetic flux of the same circuit. The reluctance in the DC field is expressed as
Where, S – reluctance in ampere-turns per weber.
F – magnetic motive force
Φ – magnetic flux
F – magnetic motive force
Φ – magnetic flux
The non-uniform magnetic circuit is made by adding the uniform sections having the different value of a length, cross-section area, and permeability of the magnetic circuit. The reluctance of the non-uniform circuit is calculated by adding the reluctance of the uniform section of the magnetic circuit. The calculation of the non-uniform magnetic field is more complex as compared to the uniform magnetic field.
In most of the transformer, an air gap is created for reducing the effects of the saturations. The air gap increases the reluctance of the circuit and hence stores the more magnetic energy before the saturation.
No comments:
Post a Comment